Frequently Asked Questions¶
Contents
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the key idea of Snakemake workflows?
- What is the recommended way to distribute a Snakemake workflow?
- My shell command fails with with errors about an “unbound variable”, what’s wrong?
- How do I run my rule on all files of a certain directory?
- Snakemake complains about a cyclic dependency or a PeriodicWildcardError. What can I do?
- Is it possible to pass variable values to the workflow via the command line?
- I get a NameError with my shell command. Are braces unsupported?
- How do I incorporate files that do not follow a consistent naming scheme?
- How do I force Snakemake to rerun all jobs from the rule I just edited?
- How do I enable syntax highlighting in Vim for Snakefiles?
- I want to import some helper functions from another python file. Is that possible?
- How can I run Snakemake on a cluster where its main process is not allowed to run on the head node?
- Can the output of a rule be a symlink?
- Can the input of a rule be a symlink?
- I would like to receive a mail upon snakemake exit. How can this be achieved?
- I want to pass variables between rules. Is that possible?
- Why do my global variables behave strangely when I run my job on a cluster?
- I want to configure the behavior of my shell for all rules. How can that be achieved with Snakemake?
- Some command line arguments like –config cannot be followed by rule or file targets. Is that intended behavior?
- How do I make my rule fail if an output file is empty?
- How does Snakemake lock the working directory?
- Snakemake does not trigger re-runs if I add additional input files. What can I do?
- How do I trigger re-runs for rules with updated code or parameters?
- How do I remove all files created by snakemake, i.e. like
make clean
What is the key idea of Snakemake workflows?¶
The key idea is very similar to GNU Make. The workflow is determined automatically from top (the files you want) to bottom (the files you have), by applying very general rules with wildcards you give to Snakemake:
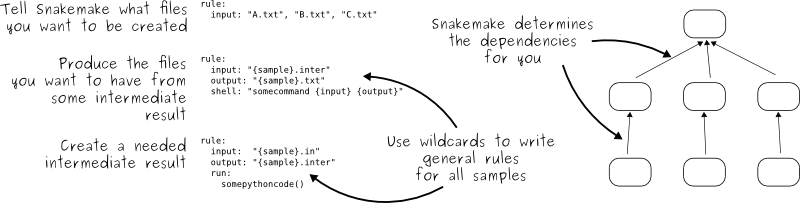
When you start using Snakemake, please make sure to walk through the official tutorial. It is crucial to understand how to properly use the system.
What is the recommended way to distribute a Snakemake workflow?¶
It is recommended that a Snakemake workflow is structured in the following way:
├── config.yaml
├── environment.yaml
├── scripts
│ ├── script1.py
│ └── script2.R
└── Snakefile
This structure can be put into a git repository, allowing to setup the workflow with the following steps:
# clone workflow into working directory
git clone https://bitbucket.org/user/myworkflow.git path/to/workdir
cd path/to/workdir
# edit config as needed
vim config.yaml
# install dependencies into an isolated conda environment
conda env create -n myworkflow --file environment.yaml
# activate environment
source activate myworkflow
# execute workflow
snakemake -n
In certain cases, it might be necessary to extend or modify a given workflow (the Snakefile). Here, git provides the ideal mechanisms to track such changes. Any modifications can happen in either a separate branch or a fork. When the changes are general enough, they can be reintegrated later into the master branch using pull requests.
My shell command fails with with errors about an “unbound variable”, what’s wrong?¶
This happens often when calling virtual environments from within Snakemake. Snakemake is using bash strict mode, to ensure e.g. proper error behavior of shell scripts. Unfortunately, virtualenv and some other tools violate bash strict mode. he quick fix for virtualenv is to temporarily deactivate the check for unbound variables
set +u; source /path/to/venv/bin/activate; set -u
For more details on bash strict mode, see the here.
How do I run my rule on all files of a certain directory?¶
In Snakemake, similar to GNU Make, the workflow is determined from the top, i.e. from the target files. Imagine you have a directory with files 1.fastq, 2.fastq, 3.fastq, ..., and you want to produce files 1.bam, 2.bam, 3.bam, ... you should specify these as target files, using the ids 1,2,3,.... You could end up with at least two rules like this (or any number of intermediate steps):
IDS = "1 2 3 ...".split() # the list of desired ids
# a pseudo-rule that collects the target files
rule all:
input: expand("otherdir/{id}.bam", id=IDS)
# a general rule using wildcards that does the work
rule:
input: "thedir/{id}.fastq"
output: "otherdir/{id}.bam"
shell: "..."
Snakemake will then go down the line and determine which files it needs from your initial directory.
In order to infer the IDs from present files, Snakemake provides the glob_wildcards function, e.g.
IDS, = glob_wildcards("thedir/{id}.fastq")
The function matches the given pattern against the files present in the filesystem and thereby infers the values for all wildcards in the pattern. A named tuple that contains a list of values for each wildcard is returned. Here, this named tuple has only one item, that is the list of values for the wildcard {id}.
Snakemake complains about a cyclic dependency or a PeriodicWildcardError. What can I do?¶
One limitation of Snakemake is that graphs of jobs have to be acyclic (similar to GNU Make). This means, that no path in the graph may be a cycle. Although you might have considered this when designing your workflow, Snakemake sometimes runs into situations where a cyclic dependency cannot be avoided without further information, although the solution seems obvious for the developer. Consider the following example:
rule all:
input:
"a"
rule unzip:
input:
"{sample}.tar.gz"
output:
"{sample}"
shell:
"tar -xf {input}"
If this workflow is executed with
snakemake -n
two things may happen.
If the file
a.tar.gzis present in the filesystem, Snakemake will propose the following (expected and correct) plan:rule a: input: a.tar.gz output: a wildcards: sample=a localrule all: input: a Job counts: count jobs 1 a 1 all 2If the file
a.tar.gzis not present and cannot be created by any other rule than rulea, Snakemake will try to run ruleaagain, with{sample}=a.tar.gz. This would infinitely go on recursively. Snakemake detects this case and produces aPeriodicWildcardError.
In summary, PeriodicWildcardErrors hint to a problem where a rule or a set of rules can be applied to create its own input. If you are lucky, Snakemake can be smart and avoid the error by stopping the recursion if a file exists in the filesystem. Importantly, however, bugs upstream of that rule can manifest as PeriodicWildcardError, although in reality just a file is missing or named differently.
In such cases, it is best to restrict the wildcard of the output file(s), or follow the general rule of putting output files of different rules into unique subfolders of your working directory. This way, you can discover the true source of your error.
Is it possible to pass variable values to the workflow via the command line?¶
Yes, this is possible. Have a look at Configuration. Previously it was necessary to use environment variables like so: E.g. write
$ SAMPLES="1 2 3 4 5" snakemake
and have in the Snakefile some Python code that reads this environment variable, i.e.
SAMPLES = os.environ.get("SAMPLES", "10 20").split()
I get a NameError with my shell command. Are braces unsupported?¶
You can use the entire Python format minilanguage in shell commands. Braces in shell commands that are not intended to insert variable values thus have to be escaped by doubling them:
...
shell: "awk '{{print $1}}' {input}"
Here the double braces are escapes, i.e. there will remain single braces in the final command. In contrast, {input} is replaced with an input filename.
How do I incorporate files that do not follow a consistent naming scheme?¶
The best solution is to have a dictionary that translates a sample id to the inconsistently named files and use a function (see Functions as Input Files) to provide an input file like this:
FILENAME = dict(...) # map sample ids to the irregular filenames here
rule:
# use a function as input to delegate to the correct filename
input: lambda wildcards: FILENAME[wildcards.sample]
output: "somefolder/{sample}.csv"
shell: ...
How do I force Snakemake to rerun all jobs from the rule I just edited?¶
This can be done by invoking Snakemake with the --forcerules or -R flag, followed by the rules that should be re-executed:
$ snakemake -R somerule
This will cause Snakemake to re-run all jobs of that rule and everything downstream (i.e. directly or indirectly depending on the rules output).
How do I enable syntax highlighting in Vim for Snakefiles?¶
A vim syntax highlighting definition for Snakemake is available here.
You can copy that file to $HOME/.vim/syntax directory and add
au BufNewFile,BufRead Snakefile set syntax=snakemake
au BufNewFile,BufRead *.rules set syntax=snakemake
au BufNewFile,BufRead *.snakefile set syntax=snakemake
au BufNewFile,BufRead *.snake set syntax=snakemake
to your $HOME/.vimrc file. Highlighting can be forced in a vim session with :set syntax=snakemake.
I want to import some helper functions from another python file. Is that possible?¶
Yes, from version 2.4.8 on, Snakemake allows to import python modules (and also simple python files) from the same directory where the Snakefile resides.
How can I run Snakemake on a cluster where its main process is not allowed to run on the head node?¶
This can be achived by submitting the main Snakemake invocation as a job to the cluster. If it is not allowed to submit a job from a non-head cluster node, you can provide a submit command that goes back to the head node before submitting:
qsub -N PIPE -cwd -j yes python snakemake --cluster "ssh user@headnode_address 'qsub -N pipe_task -j yes -cwd -S /bin/sh ' " -j
This hint was provided by Inti Pedroso.
Can the output of a rule be a symlink?¶
Yes. As of Snakemake 3.8, output files are removed before running a rule and then touched after the rule completes to ensure they are newer than the input. Symlinks are treated just the same as normal files in this regard, and Snakemake ensures that it only modifies the link and not the target when doing this.
Here is an example where you want to merge N files together, but if N == 1 a symlink will do. This is easier than attempting to implement workflow logic that skips the step entirely. Note the -r flag, supported by modern versions of ln, is useful to achieve correct linking between files in subdirectories.
rule merge_files:
output: "{foo}/all_merged.txt"
input: my_input_func # some function that yields 1 or more files to merge
run:
if len(input) > 1:
shell("cat {input} | sort > {output}")
else:
shell("ln -sr {input} {output}")
Do be careful with symlinks in combination with Step 6: Temporary and protected files. When the original file is deleted, this can cause various errors once the symlink does not point to a valid file any more.
If you get a message like Unable to set utime on symlink .... Your Python build does not support it. this means that Snakemake is unable to properly adjust the modification time of the symlink.
In this case, a workaround is to add the shell command touch -h {output} to the end of the rule.
Can the input of a rule be a symlink?¶
Yes. In this case, since Snakemake 3.8, one extra consideration is applied. If either the link itself or the target of the link is newer than the output files for the rule then it will trigger the rule to be re-run.
I would like to receive a mail upon snakemake exit. How can this be achieved?¶
On unix, you can make use of the commonly pre-installed mail command:
snakemake 2> snakemake.log
mail -s "snakemake finished" youremail@provider.com < snakemake.log
In case your administrator does not provide you with a proper configuration of the sendmail framework, you can configure mail to work e.g. via Gmail (see here).
I want to pass variables between rules. Is that possible?¶
Because of the cluster support and the ability to resume a workflow where you stopped last time, Snakemake in general should be used in a way that information is stored in the output files of your jobs. Sometimes it might though be handy to have a kind of persistent storage for simple values between jobs and rules. Using plain python objects like a global dict for this will not work as each job is run in a separate process by snakemake. What helps here is the PersistentDict from the pytools package. Here is an example of a Snakemake workflow using this facility:
from pytools.persistent_dict import PersistentDict
storage = PersistentDict("mystorage")
rule a:
input: "test.in"
output: "test.out"
run:
myvar = storage.fetch("myvar")
# do stuff
rule b:
output: temp("test.in")
run:
storage.store("myvar", 3.14)
Here, the output rule b has to be temp in order to ensure that myvar is stored in each run of the workflow as rule a relies on it. In other words, the PersistentDict is persistent between the job processes, but not between different runs of this workflow. If you need to conserve information between different runs, use output files for them.
Why do my global variables behave strangely when I run my job on a cluster?¶
This is closely related to the question above. Any Python code you put outside of a rule definition is normally run once before Snakemake starts to process rules, but on a cluster it is re-run again for each submitted job, because Snakemake implements jobs by re-running itself.
Consider the following...
from mydatabase import get_connection
dbh = get_connection()
latest_parameters = dbh.get_params().latest()
rule a:
input: "{foo}.in"
output: "{foo}.out"
shell: "do_op -params {latest_parameters} {input} {output}"
When run a single machine, you will see a single connection to your database and get a single value for latest_parameters for the duration of the run. On a cluster you will see a connection attempt from the cluster node for each job submitted, regardless of whether it happens to involve rule a or not, and the parameters will be recalculated for each job.
I want to configure the behavior of my shell for all rules. How can that be achieved with Snakemake?¶
You can set a prefix that will prepended to all shell commands by adding e.g.
shell.prefix("set -o pipefail; ")
to the top of your Snakefile. Make sure that the prefix ends with a semicolon, such that it will not interfere with the subsequent commands. To simulate a bash login shell, you can do the following:
shell.executable("/bin/bash")
shell.prefix("source ~/.bashrc; ")
Some command line arguments like –config cannot be followed by rule or file targets. Is that intended behavior?¶
This is a limitation of the argparse module, which cannot distinguish between the perhaps next arg of --config and a target.
As a solution, you can put the –config at the end of your invocation, or prepend the target with a single --, i.e.
$ snakemake --config foo=bar -- mytarget
$ snakemake mytarget --config foo=bar
How do I make my rule fail if an output file is empty?¶
Snakemake expects shell commands to behave properly, meaning that failures should cause an exit status other than zero. If a command does not exit with a status other than zero, Snakemake assumes everything worked fine, even if output files are empty. This is because empty output files are also a reasonable tool to indicate progress where no real output was produced. However, sometimes you will have to deal with tools that do not properly report their failure with an exit status. Here, the recommended way is to use bash to check for non-empty output files, e.g.:
rule:
input: ...
output: "my/output/file.txt"
shell: "somecommand {input} {output} && [[ -s {output} ]]"
How does Snakemake lock the working directory?¶
Per default, Snakemake will lock a working directory by output and input files. Two Snakemake instances that want to create the same output file are not possible. Two instances creating disjoint sets of output files are possible.
With the command line option --nolock, you can disable this mechanism on your own risk. With --unlock, you can be remove a stale lock. Stale locks can appear if your machine is powered off with a running Snakemake instance.
Snakemake does not trigger re-runs if I add additional input files. What can I do?¶
Snakemake has a kind of “lazy” policy about added input files if their modification date is older than that of the output files. One reason is that information what to do cannot be inferred just from the input and output files. You need additional information about the last run to be stored. Since behaviour would be inconsistent between cases where that information is available and where it is not, this functionality has been encoded as an extra switch. To trigger updates for jobs with changed input files, you can use the command line argument –list-input-changes in the following way:
$ snakemake -n -R `snakemake --list-input-changes`
Here, snakemake --list-input-changes returns the list of output files with changed input files, which is fed into -R to trigger a re-run.
How do I trigger re-runs for rules with updated code or parameters?¶
Similar to the solution above, you can use
$ snakemake -n -R `snakemake --list-params-changes`
and
$ snakemake -n -R `snakemake --list-code-changes`
Again, the list commands in backticks return the list of output files with changes, which are fed into -R to trigger a re-run.
How do I remove all files created by snakemake, i.e. like make clean¶
To remove all files created by snakemake as output files to start from scratch, you can use
rm $(snakemake --summary | tail -n+2 | cut -f1)